Systolic blood pressure and outcomes in acute coronary syndromes
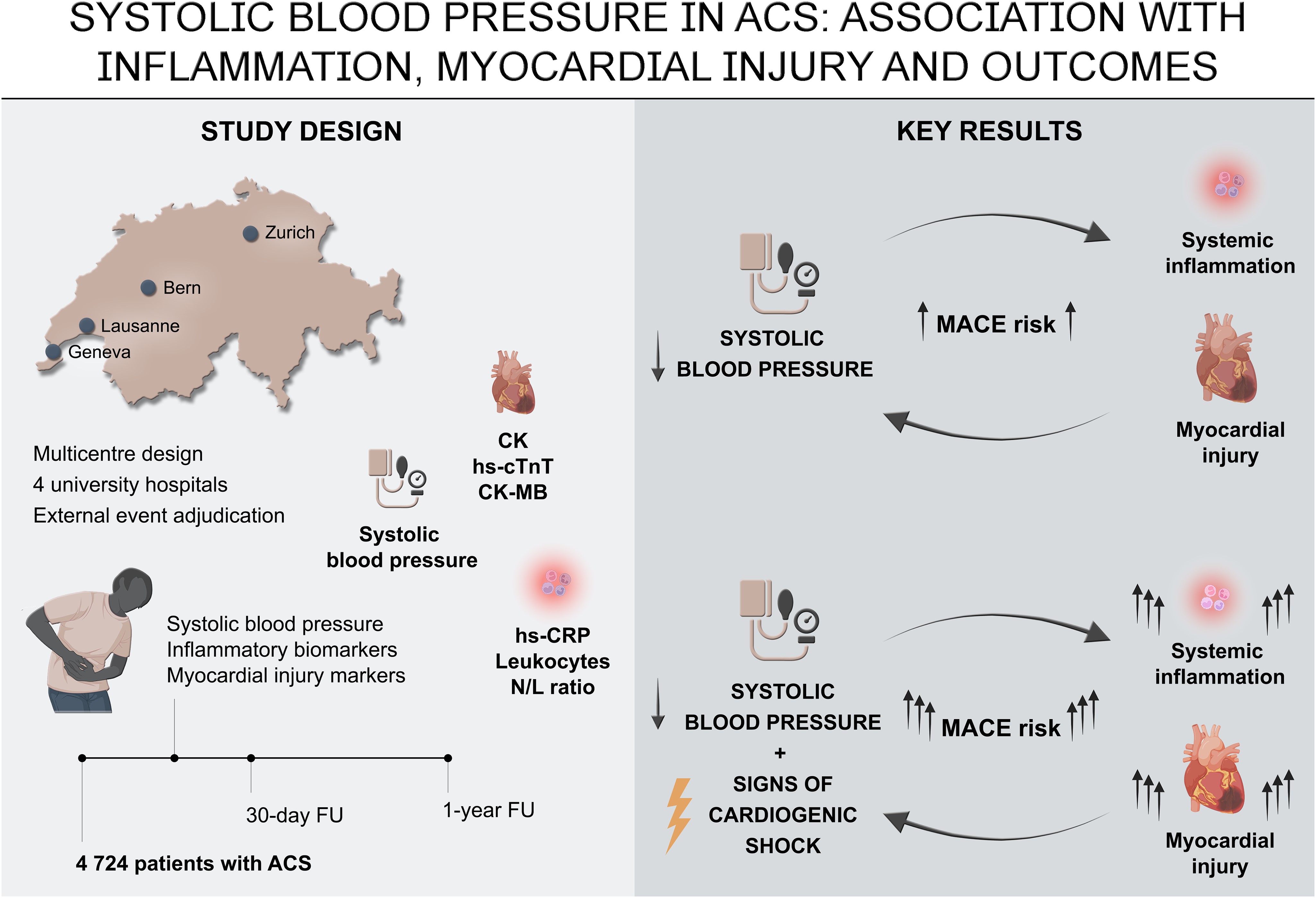
Outcomes after acute coronary syndromes (ACS) are determined by baseline risk profiles, including initial systolic blood pressure (sBP). Herein, we aimed to characterize ACS patients stratified by initial sBP levels and study the relation to inflammation, myocardial injury and post-ACS outcomes. We analysed 4'724 prospectively recruited ACS patients according to invasively assessed sBP (<100, 100-139, and ≥140mmHg) at admission. Biomarkers of systemic inflammation (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, hs-CRP) and myocardial injury (high-sensitivity cardiac troponin, hs-cTnT) were measured centrally. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE; non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), non-fatal stroke and cardiovascular (CV) death) were externally adjudicated. Notably, proxies of systemic inflammation and myocardial injury were inversely associated with sBP, with highest levels in those <100mmHg. If linked to high levels of cellular inflammation, these patients were prone to develop cardiogenic shock and were at high MACE and mortality risk. Full study results are now available at Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care.
Simon Kraler